Stonehenge Exhibition is an immersive, interactive experience that brings the mysteries of the enigmatic monument to life.
Visitors of all ages can explore the world behind the stones, uncovering the secrets of their builders, the landscape and its place in the wider world.
Through interactive displays, archaeology and cutting-edge audio-visual experiences, visitors can uncover the stories behind the stones and the meaning of Stonehenge.
The incredible artifacts on display are listed here.
Polished axes
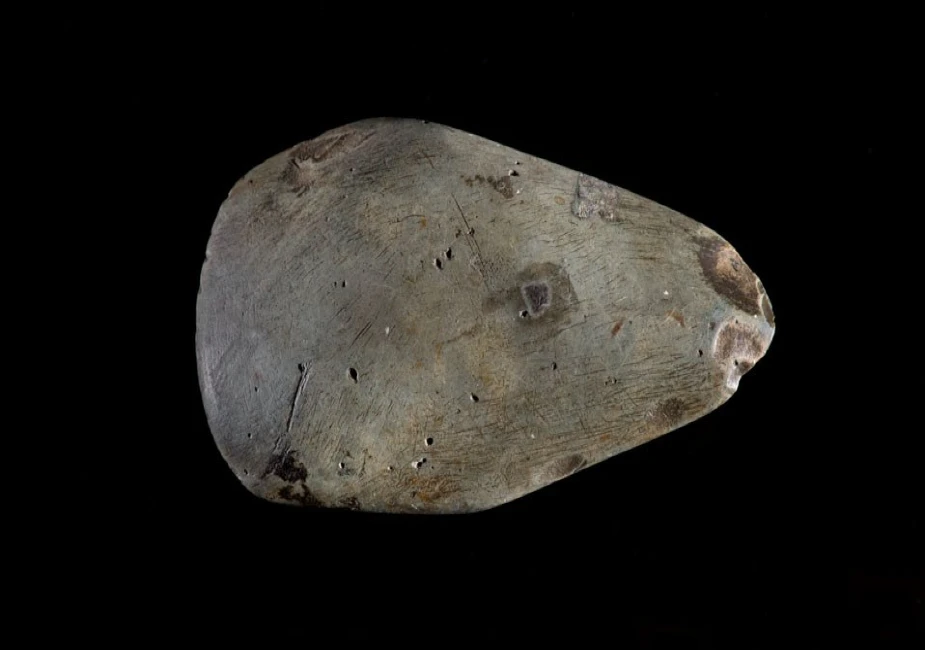

The Polished Axe from the Stonehenge World Heritage Site is a rare example of an early Neolithic tool.
People made this object from stone from the Great Langdale in Cumbria, dating from c 4000 BC.
The early Neolithic farming communities likely used this axe to clear woodland, an essential task.
Traders widely distributed axes from stone sourced from the Great Langdale in Cumbria across Britain.
Flint knapping groups
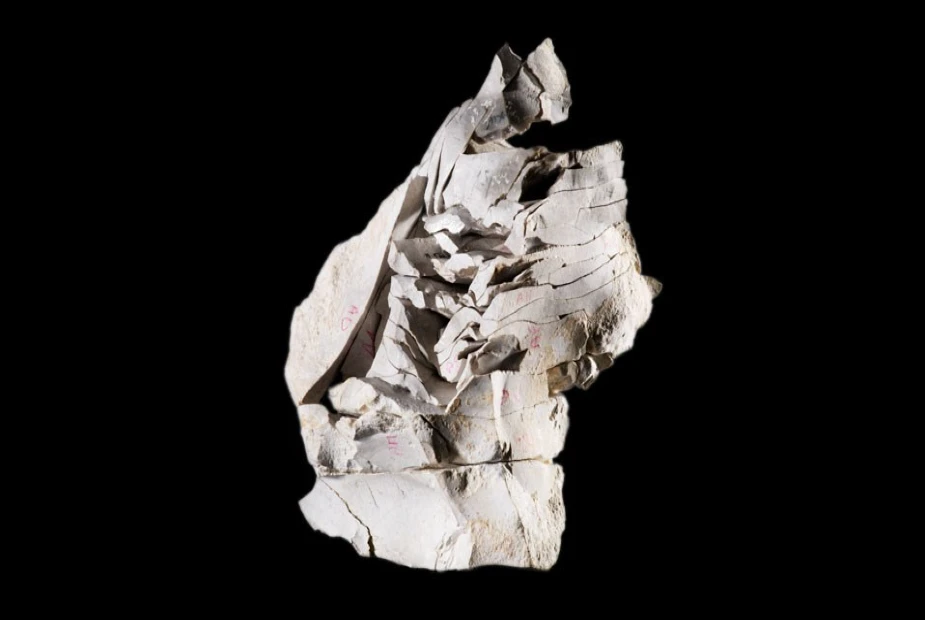

Flint knapping is the ancient art of shaping flint or stone into tools, weapons and ornaments.
In 1997, archaeologists discovered the Amesbury 42-long barrow ditch, which contained several flint tools and a lump of flint from which they reconstructed this piece.
The Salisbury & South Wiltshire Museum dedicates its flint knapping group to preserving and passing on this ancient art form.
They demonstrate how traditional methods and tools can flint knap and make stone tools and weapons.
Mandibles
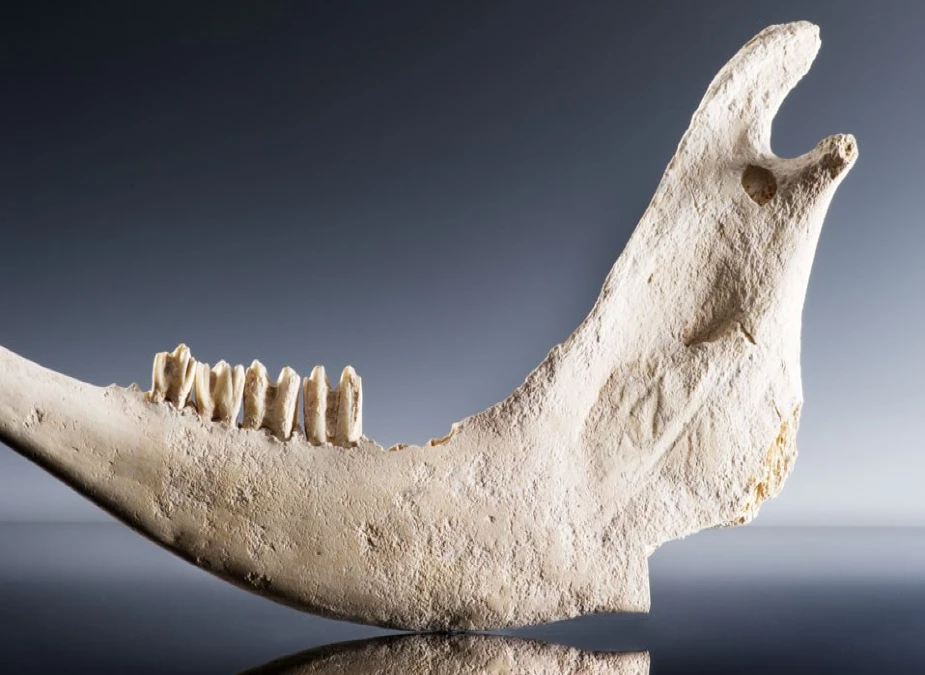
The mandible (lower jaw bone) is from domestic cattle and is the only bone found at Stonehenge.
Archaeologists found a pottery fragment at the base of the Stonehenge ditch that dates back to around 3300 BC.
The mandible was made from domestic cattle bone, measuring 8 cm wide and 5 cm long.
The teeth are well-worn, indicating that the animal was probably quite old when it died.
This jawbone is integral to Stonehenge’s history and provides clues as to its significance to its builders.
Antler picks
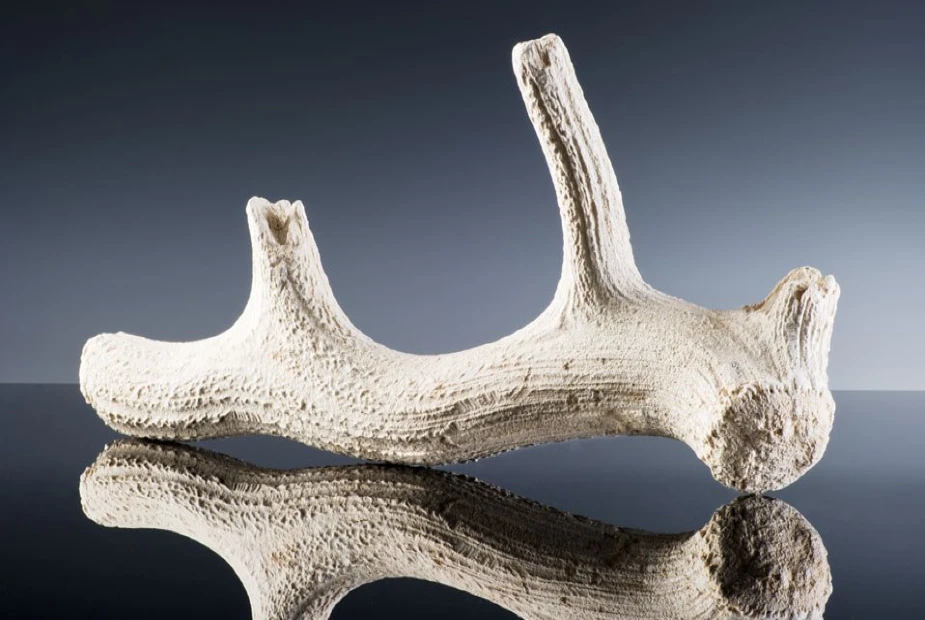
Estimated to date at 3000 BC, people who built Stonehenge left an antler pick in the Stonehenge ditch in Wiltshire, England, as an offering or ritual deposit.
Evidence shows that the pick, made of red deer antlers, was used to dig the ditch and shape the chalk and its worn points indicate its purpose.
This artifact links to the past, revealing the monument’s importance and the beliefs of its builders.
Chalk plaques

The Chalk Plaque is found 2km from Stonehenge and dates back to 2900-2580 BC.
The chalk was decorated with incised lines and marks, providing a unique glimpse into the past and showing the sophistication and creativity of the people who made it.
Despite its mysterious purpose and meaning, its importance lies in its rarity as one of the earliest known examples of British art.
The Salisbury and South Wiltshire Museum has loaned it as part of its permanent exhibition.
Arrowheads
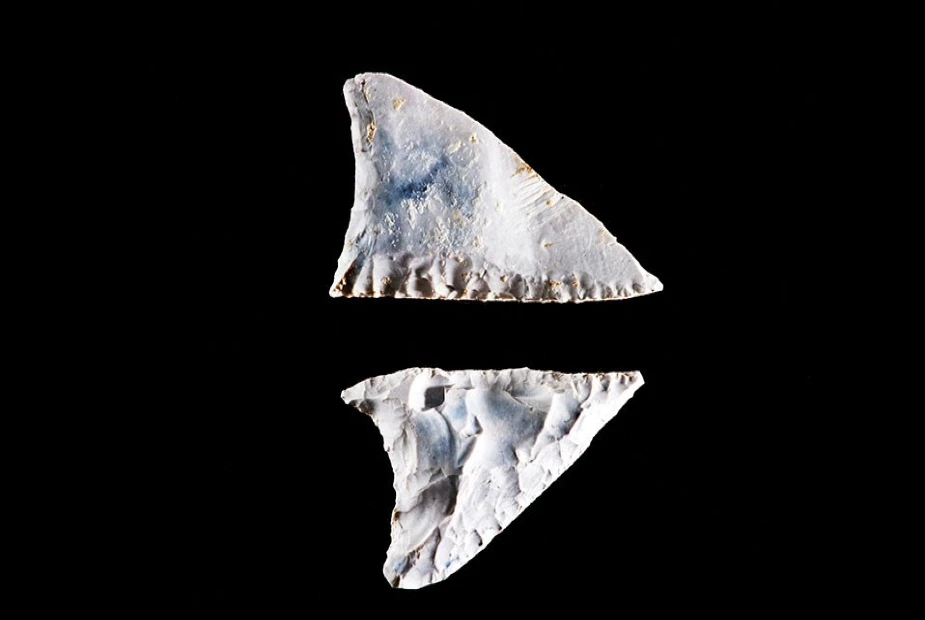

An excavation at Durrington Walls, a famous Neolithic henge monument near Stonehenge, yielded this arrowhead.
The arrowhead is part of a collection of objects from the site. Dating from around 2500 BC, the arrowhead is made from local flint and is lop-sided, or ‘oblique.’
During the Neolithic period, people commonly used oblique arrowheads as a type of flint tool.
Their lop-sided shape characterizes them and makes them ideal for piercing the skin of animals.
This type of arrowhead was used for hunting and killing pigs, which were then cooked and eaten during great feasts.
The arrowhead is a reminder of how ancient people used to live and hunt in the area.
Pig legs with embedded arrows
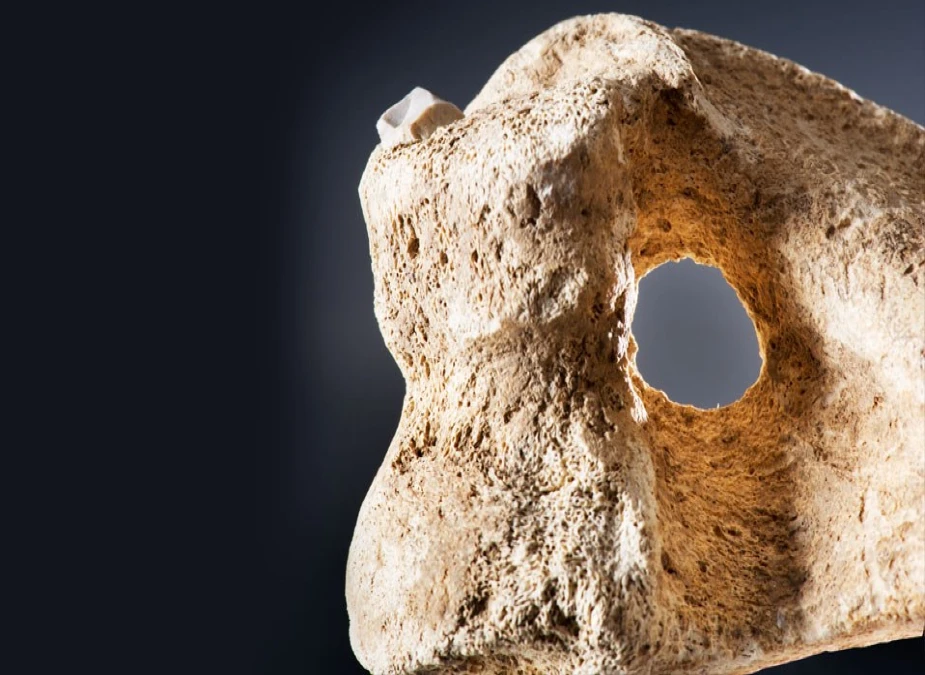

The pig leg, with a flint arrow embedded in the bone, is an excellent example of how the people of Durrington Walls incorporated their hunting and feasting rituals.
It is a remarkable reminder of prehistoric peoples’ vibrant culture and spirituality.
The pig leg with an embedded arrow is an iconic symbol of the Neolithic era.
It demonstrates the importance of hunting and feasting to the people of Durrington Walls and reflects their close connection to the land and their animals.
It reminds them how their rituals and traditions have been preserved and passed down.
Grooved ware sherds
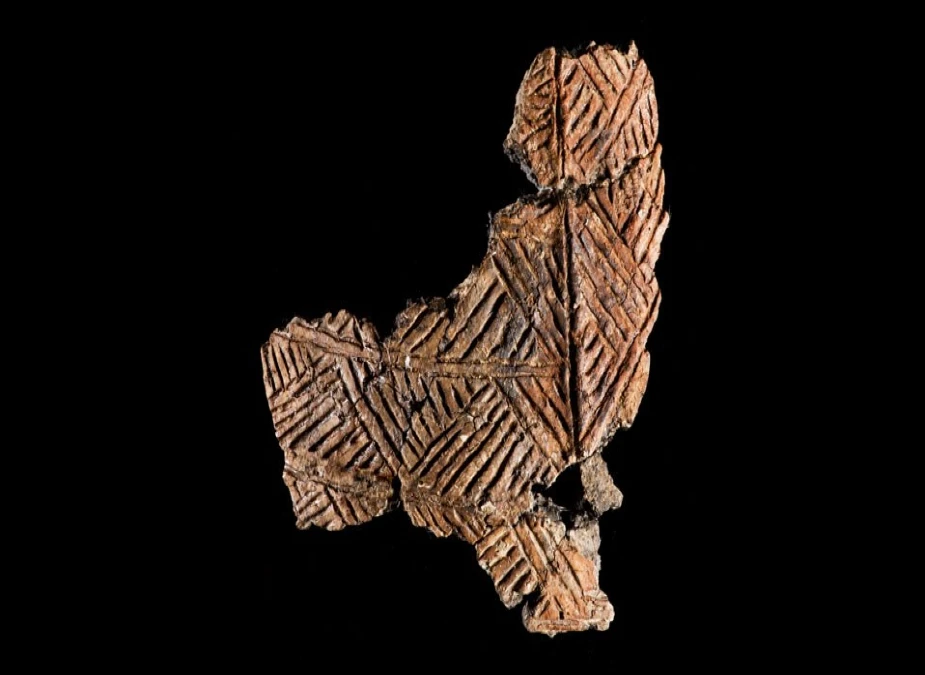

The grooved ware sherds from Woodhenge are unique, as they are among Britain’s oldest pottery pieces. The sherds were found during a dig in the 1970s.
The sherds show evidence of having been used in a ritual context.
The symbols are abstract, with curved and straight lines, circles and impressions.
These symbols likely had some meaning to the people who used them.
The sherds have also been used to date Woodhenge to the late Neolithic period.
The sherds are comparable to other objects found in the area, suggesting that the same people were living in the area and following similar practices.
Battle Axe
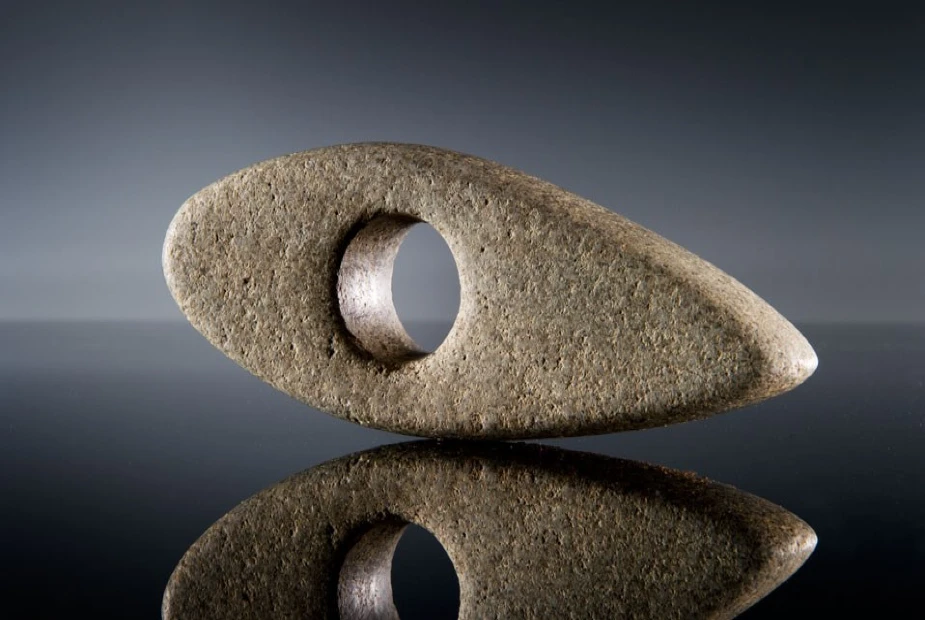

The battle axe was a standard weapon in the Bronze Age, but the careful craftsmanship of this one suggests it was of ceremonial use.
It is small and delicate, more suitable for display than use in battle.
The axe head is decorated with circles and concentric arcs that may have had symbolic significance.
The battle axe is a reminder of Stonehenge’s importance in Prehistoric Britain and a testimony to prehistoric artisans’ skill.
It is a unique object and is now on display at the Wiltshire Museum in Devizes.
Circle of Stone Exhibition
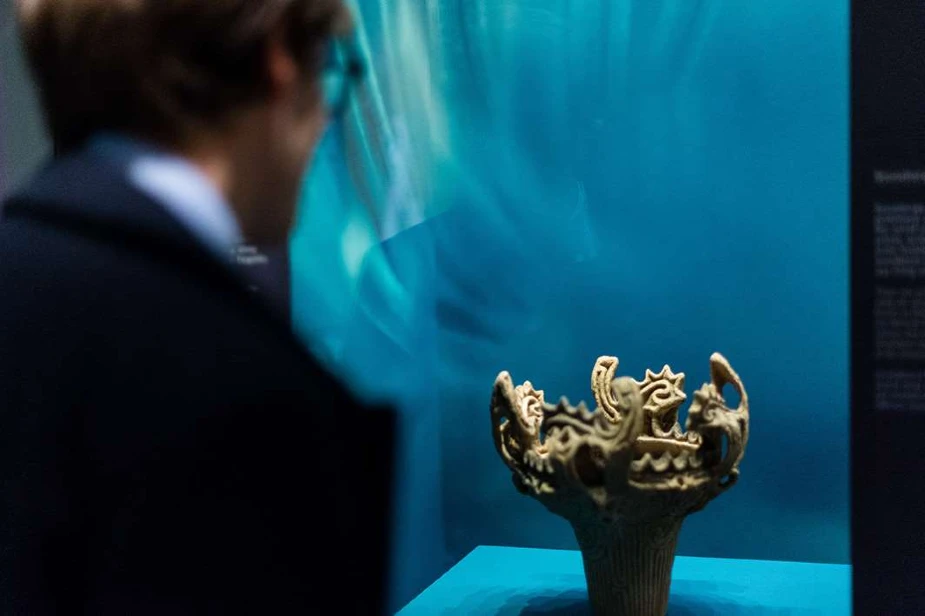

The exhibition commemorates Japan’s history in the Middle and Late Jomon periods, around the same period as when Stonehenge was constructed.
The exhibition showcases a selection of artifacts, some unseen outside Japan, that tell the story of settlements and stone circles from this era.
- Flame pots
- Dogu masks
- Carved bears
- Counting dog
- Jomon stone axes
- Neolithic houses
Featured Image: English.elpais.com



